What is Formwork
DOWNLOAD FULL EBOOK HERE
Formwork is a die or a mould including all supporting structures, used to shape and support the concrete
until it attains sufficient strength to carry its own weight. It should be capable of carrying all imposed dead
and live loads apart from its own weight.
INTRODUCTION TO FORMWORK
Formwork has been in use since the beginning of concrete construction.
New materials such as steel, plastics and fiberglass are used in formwork.
Greater attention is being given to the design, fabrication, erection and dismantling of formwork
DEFENITION:
As a structure,
Temporary which is designed to contain fresh fluid concrete.
Form it into the required shape and dimensions.
Support it until it cures sufficiently to become self supporting.
The term ‘formwork’ includes the actual material contact with the concrete, known asform face, and all the
necessary associated supporting structure.
REQUIREMENTS OF A GOOD FORMWORK SYSTEM
How formwork can be erected and de-shuttered fast.
How good concrete quality and surface finish can be achieved.
What is the optimum stock of formwork required for the size of work force, the specified time schedule and flow of materials.
What is the overall cost savings that can be achieved using the right typeof formwork.
How SAFETY can be improved for the site personnel.
In order to successfully carry out its function, formwork must achieve a balance of following requirements:
Containment
Strength
Resistance To Leakage
Accuracy
Ease Of Handling
Finish And Reuse Potential
Access For Concerted
Economy
Containment: formwork must be capable of shaping and supporting the fluid concrete until it cures.
Strength: formwork must be capable of safely withstanding without distortion or danger the dead weight of
the fluid concrete is placed on it, labour weight, equipment weight and any environmental loadings.
Resistance to leakage: all joints in form work must be either close fitting of covered with form tape to
make them grout tight. If grout leakage occurs the concrete Will leak at that point. Leakages cause
honeycombing of the surface.
Accuracy: formwork must be accurately set out so that the resulting concrete productis in a right place
and is of correct shape and dimensions.
Ease of handling: form panels and units should be designed so that their maximum size does not exceed
that which can be easily handled by hand or mechanical means. In addition all formwork must also be
designed and constructed to include facilities for adjustments, leveling, easing and striking without
damage to the form work or concrete.
Finish and reuse potential: the form face material must be selected to be capable of consistently
imparting the desired concrete finish (smooth, textured, featured or exposed aggregate etc.) At the same
time it should also achieve the required number of reuse.
Access for concrete: any formwork arrangement must be provide access for placing of the concrete. The
extent of this provision will be dependent on the ease of carrying out the concrete operations.
Economy: all the formwork is very expensive. On average about 35% of the total cost of any finished
concrete unit or element can be attributed to its formwork; of this just over 40% can be taken for material
for formwork and 60% for labour. The formwork designer must therefore not only consider the maximum
number of times that any form can be reused, but also produce a design that will minimize the time taken
for erection and striking.
FORMWORK BASED ON MATERIALS MATERIALS FOR FORMWORK
Formwork can be made out of a large variety of materials.
The material most commonly being used to date is timber. However, due to the depleting forest reserves and increasing cost of timber the use of alternate materials such as plywood and steel has become prominent.
More recently, materials such as plastics and fiberglass are also being used for pre-fabricating formwork.
The type of material to be used depends on the nature of construction as well as availability and cost of material.
The constraints on the project such as overall cost, time of completion also play a major role in the use of a particular material for formwork.
TIMBER FORMS
Timber is required for practically all jobs of formwork. The timber bring used for formwork must satisfy the
following requirements:
I.It should be durable and treatable
II.It should have sufficient strength characteristics
III.It should be light weight and well seasoned without warping,
IV.It should hold nails well.
Advantages of using timber forms:
I.It is economical for small construction jobs
II.It is design flexible and easy to erect
III.It has good thermal insulation which makes it useful to be used in colder
Regions
IV. It can easily be made into any shape or size
Plywood forms (in combination with timber)
Concrete shuttering plywood is bwp grade plywood, preservative treated and specially suited for use in concrete shuttering and formwork.
The plywood is built up of odd number of layers with grain of adjacent layers perpendicular to each other.
Plywood is used extensively for formwork for concrete, especially for sheathing, decking and form linings.
There are two types of plywood - internal and exterior.
The interior type is bonded with water resistant glue and exterior type is bonded with water proof glue.
Hardboard forms
Hardboard is a board material manufactured of wood fiber, which is then refined or partly refined to form a panel having a density range of approximately 50 to 80 pounds per cubic foot.
Hardboards are standard / non-tempered or tempered.
The tempered one being used for formwork. Tempered hardboard is solid or perforated hardboard panels impregnated with resin under high pressure to make them stronger and more resistant to moisture and abrasion.
The boards available in large sheets have a hard, smooth surface that produces a concrete whose surface is relatively free of blemishes and joint marks.
The thin sheets can be bent to small radii, which is an advantage when casting concrete members with curved surfaces.
ALUMINIUM FORMS
Forms made from aluminum are in many respects similar to those made of steel.
However, because of their lower density, aluminum forms are lighter than steel forms, and this is their primary advantage when compared to steel.
As the strength of aluminum in handling, tension and compression is less than the strength of steel, it is necessary to use large sections.
The formwork turns out to be economical if large numbers of reuses are made in construction.
The major disadvantage of aluminum forms is that no changes can be made once the formwork is fabricated.
PLASTICS
These forms have become increasingly popular for casting unique shapes and patterns being designed in concrete because of the excellent finish obtained requiring minimum or no surface treatment and repairs.
Different types of plastic forms are available like glass reinforced plastic, fiber reinforced plastic and thermoplastics etc.
Fiberglass-reinforced plastic is the most common and has several advantages such as
I.The material allows greater freedom of design
II.Unusual textures and designs can be molded into the form
III.It allows the contractor to pour structural and finished concrete Simultaneously
IV.Because sections can be joined on the job site in such a way so as to eliminate joints, there is no size limitation If carefully handled, a number of reuses are possible making it highly Economical
VI. It is lightweight and easily stripped
The disadvantage of using plastic forms is that it does not lend itself to field fabrication Hence, the
design and planning of this form must be carefully carried out.Also care must take not to damage the
plastic by the heat applied for accelerated curing of the concrete. Trough and waffle units in fiberglass are
used in construction of large floor areas and multistoried office buildings.
STEEL FORMWORK:
Mostly used in large construction projects or in situations where large number of re-uses of the same shuttering is possible. Suitable for circular or curved shaped structures such as tanks, columns, chimneys. Etc. & for structures like sewer tunnel and retaining wall.
Advantages of steel formwork over timber form:
strong, durable & have longer life
Reuses can be assumed to vary from 100 to 120 wares timber varies from 10 to 12.
Steel can be installed & dismantled with greater ease & speed resulting in saving in labour cost.
Excellent quality of exposed concrete surface obtained. Thus saving in the cost of finishing the conc. surface.
no danger of formwork absorbing water from the conc. & hence minimizing honeycombing
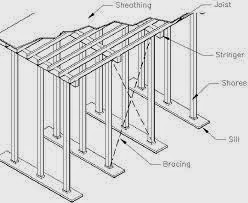
CONSTRUCTION OF FORMWORK:
• propping and centering
• shuttering
• provision of camber
• cleaning & surface treatment
Propping and centering:
The props used for centering may be of steel, timber post or ballies.pillars made up of
brick masonry in mud mortar are also sometimes used as props.
DOWNLOAD EBOOK TO READ FULL

.jpg)

Post a Comment